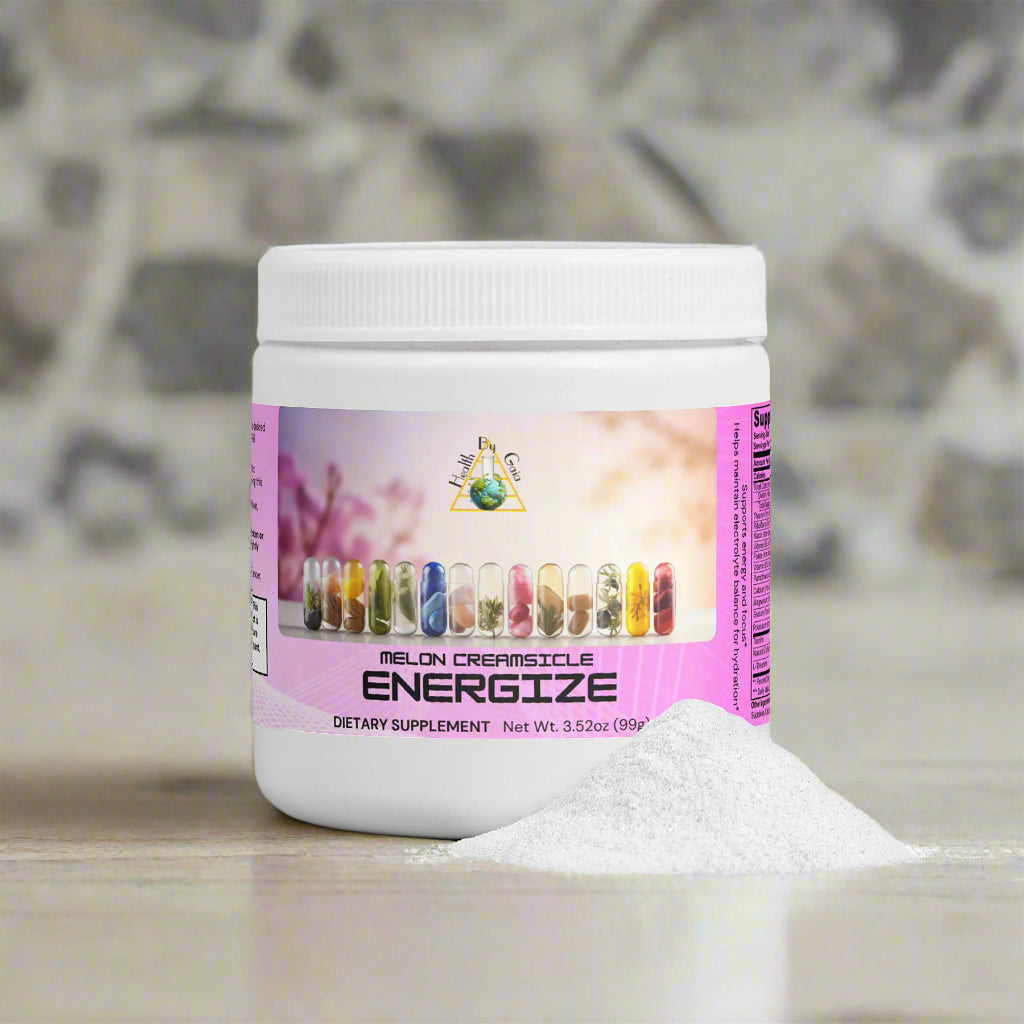
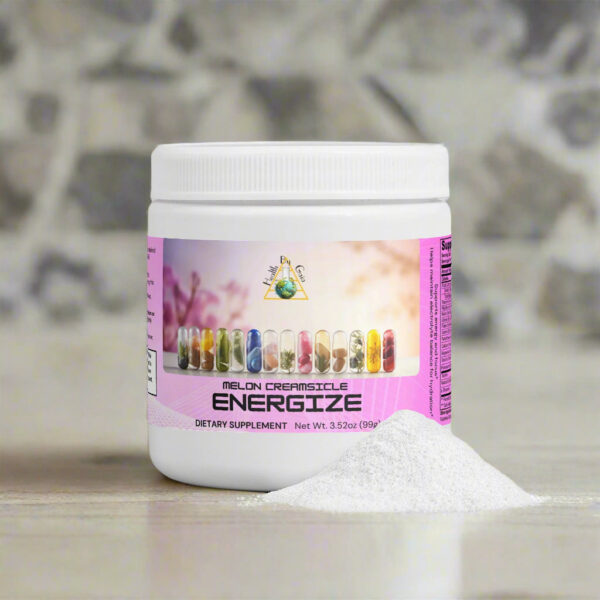
Save 20% When You Buy 2 Health By Gaia Products with 20OFFTWO | Free Shipping on US orders over $100
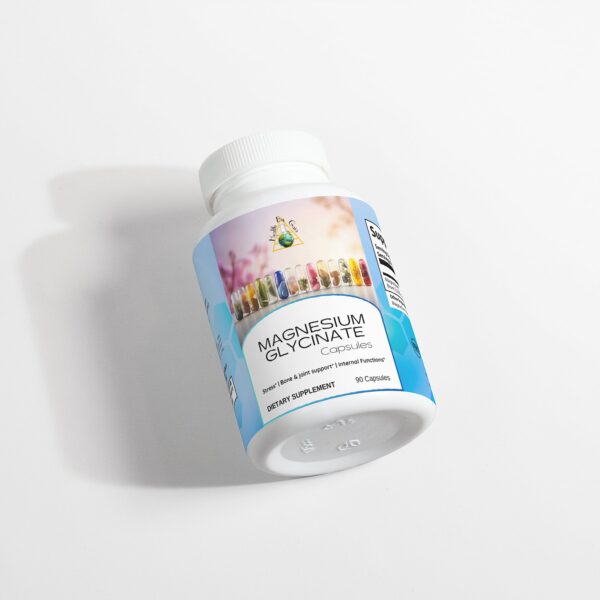
Nature’s Way Alfalfa 810mg Vegan Capsules
$20.99
SaveSaved0
CompareAdded0
Nature’s Way sources tender young plants to supply a high portion of supple leaves and to avoid the inclusion of woody stems
SKU: J3DJZ2XR7BHR
Claims for health uses are based on evidence acquired from independent and group research which showed to provide the health improvements which were ascertained from different studies of certain natural substances. It is important to note that these claims have not been evaluated or endorsed by the FDA. You should consult a physician prior to changing any prescription regimen or implementing herbal substances on top of prescribed medications. Always do research that is independent and make informed decisions based on your best judgement. Improvement or various health uses of products will only likely show results with adherence to nutrient intake.
| Supplements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| General | ||||||
|
||||||
| Dimensions | ||||||
|
||||||
Recently Viewed